The way to use urea fertilizer and its amount depend on soil analysis and the type of crop, and it is best to follow the advice of experts. Just as a plant will not grow well without fertilizer, excessive use of urea fertilizer can also harm the plant.
How to apply urea fertilizer step by step

Urea fertilizer is one of the most effective sources of nitrogen for plants. With 46% nitrogen, it is highly concentrated and economical. To use it optimally, you should pay attention to the correct methods and key points. In this guide, we will review all the steps in detail.
Step 1: Identifying the Plant’s Nitrogen Needs
Before using urea fertilizer, check how much nitrogen your plant needs. This amount varies depending on the crop type and growth stage.
Practical Example: For wheat crops, in the early stages of growth, 120-150 kg of nitrogen per hectare is required.
Mental Image: Imagine that your plants are like children, needing different kinds of nutrition at each stage of their growth.
Step 2: Soil Testing
Your agricultural soil must have the ability to absorb nitrogen. Soil testing is necessary to check the available nitrogen levels and pH.
Practical Tip: If the soil pH is higher than 7, some of the nitrogen will be lost as ammonia.
Mental Image: Think of your soil as a sponge that should be able to hold nitrogen. If it is too dry or heavy, nutrients will be wasted.
Step 3: The Right Time to Use Urea Fertilizer
The best time to use urea fertilizer varies depending on the crop:
- Before planting (pre-planting)
- After germination (early growth)
- During flowering and fruit growth
Practical Example: For corn, it is best to apply urea fertilizer in two stages: half before planting and half during the 6-8 leaf stage.
Mental Image: Like a professional cyclist, the plant needs sufficient fuel throughout its growth journey.

Step 4: Methods of Applying Urea Fertilizer
The correct method of applying urea fertilizer is crucial to prevent nitrogen evaporation.
Suggested Methods:
Surface application and tilling: Spread the urea on the soil surface, then till the soil to bury the fertilizer.
Solution injection: Dissolve urea in water and apply it to the soil through drip irrigation.
Mental Image: If the fertilizer stays on the surface, it will evaporate like ice in the sun. But if you bury it in the soil, nutrients will be available to the roots.
Step 5: Post-Application Care
After applying fertilizer, monitoring the plants is essential:
- Have the leaves turned greener and healthier?
- Has the plant’s growth improved?
- Are there any signs of nutrient deficiency or overuse?
Practical Example: If the leaves turn yellow instead of becoming green, the plant may have a potassium deficiency or nitrogen overuse.
Mental Image: Urea fertilizer is like water that should reach the plant in just the right amount; too little or too much can cause problems.
Key Tips for Preventing Nitrogen Loss
- Avoid applying urea fertilizer on dry soils.
- Do not fertilize during windy conditions.
- In sandy soils, apply fertilizer in multiple stages.

Nitrogen Requirement Table for Some Crops
| Crop | Nitrogen Amount (kg/hectare) | Application Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 120-150 | Pre-planting and flowering |
| Corn | 150-200 | 6-8 leaf stage and flowering |
| Rice | 100-120 | Pre-planting and growth stage |
Urea Fertilizer Dosage
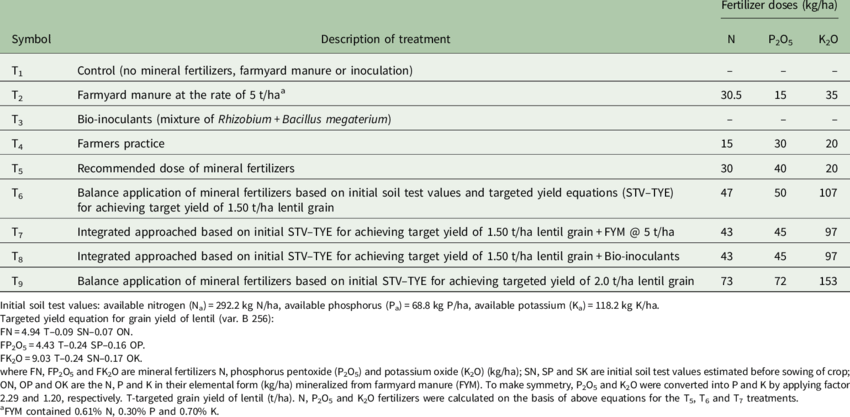
researchgate.net
Fertilizer doses as per recommended dose of fertilizers (RDF) and soil test values (STV) and targeted yield equations (TYE) of lentil
When to Use Urea Fertilizer
Urea fertilization for plants can be done either by mixing it with the soil or in combination with irrigation water. However, the irrigation should not be excessive, as ammonia loss may occur. The best method for using urea fertilizer is by spreading it on the soil either pure or mixed with other chemical fertilizers. You can also apply urea in bands, 4-5 cm away from the seeds. However, under no circumstances should urea be used next to corn. Urea can be mixed with monoammonium phosphate or diammonium phosphate, but it should not be mixed with superphosphates, as the reaction between urea and superphosphates releases water, making the mixture moist and unsuitable for storage or spreading.

how to use urea fertilizer
When urea fertilizer is applied to the soil, it undergoes changes, forming ammonium ions, and the pH of the surrounding areas increases. As the concentration of ammonia rises, the area becomes toxic for a few hours, but this toxicity is neutralized once ammonia converts into ammonium. It is best to plant seeds and seedlings several hours after urea fertilization because plants only have a few days to effectively utilize the nitrogen from this fertilizer. For crops like potatoes and soybeans, foliar application of urea should be used, but the nitrogen amount should not exceed 9 or 10 kg per hectare.
Methods of Using Urea Fertilizer for Plants
There are various methods of applying fertilizer to plants, and these methods can change depending on the type of fertilizer and its absorption by the plant. Urea fertilizer is commonly applied using the following two methods:
Foliar Application: In this method, urea is dissolved in water and sprayed as a solution onto the stems and leaves of the plants. The plants absorb the fertilizer directly through the stem and leaves. This method is commonly used for vegetables and some cereals, such as wheat. Potatoes and soybeans are other crops that are fertilized using the foliar application method. This method is also used for other fertilizers, such as urea phosphate.
Soil Injection: In this method, the fertilizer is directly applied to the soil, where urea decomposes into nitrate and ammonium, providing the nutrients required by the plants. Since the enzymatic reaction of the soil to decompose urea takes time, research has shown that nutrient absorption from this fertilizer is more efficient and easier for plants.

When to Use Urea Fertilizer
Many farmers apply urea before planting or during the planting of crops. However, due to the high potential for leaching and volatilization of this fertilizer, it is best not to use it at the time of planting or just before planting. This is because, until the seed germinates, sprouts, and can absorb the nutrients, the fertilizer may be lost from the soil. Therefore, in such cases, slow-release fertilizers are a better option.
Best Time to Apply Urea Fertilizer
urea fertilizer application time: One of the most important questions regarding urea fertilizer is the optimal time for application. It is possible to detect soil deficiencies by observing the appearance of the soil, the plant’s growth, and through soil testing, and apply fertilizer if necessary. However, some plants, due to their high nutrient requirements, need to be fertilized with urea at different stages. For example:
urea fertilizer application time
- Cotton at the time of planting
- Wheat during germination
- Vegetables during the growing season
In cold seasons, because urea tends to convert into ammonia, the soil often suffers from nitrogen deficiency. Therefore, it is essential to regularly measure and balance the levels of this fertilizer in the soil. Sometimes, this imbalance can cause the soil to become either acidic or alkaline. Urea can also be used like phosphoric acid in acidic soils to help adjust the soil’s pH.
Recommended Rate of Urea Fertilizer
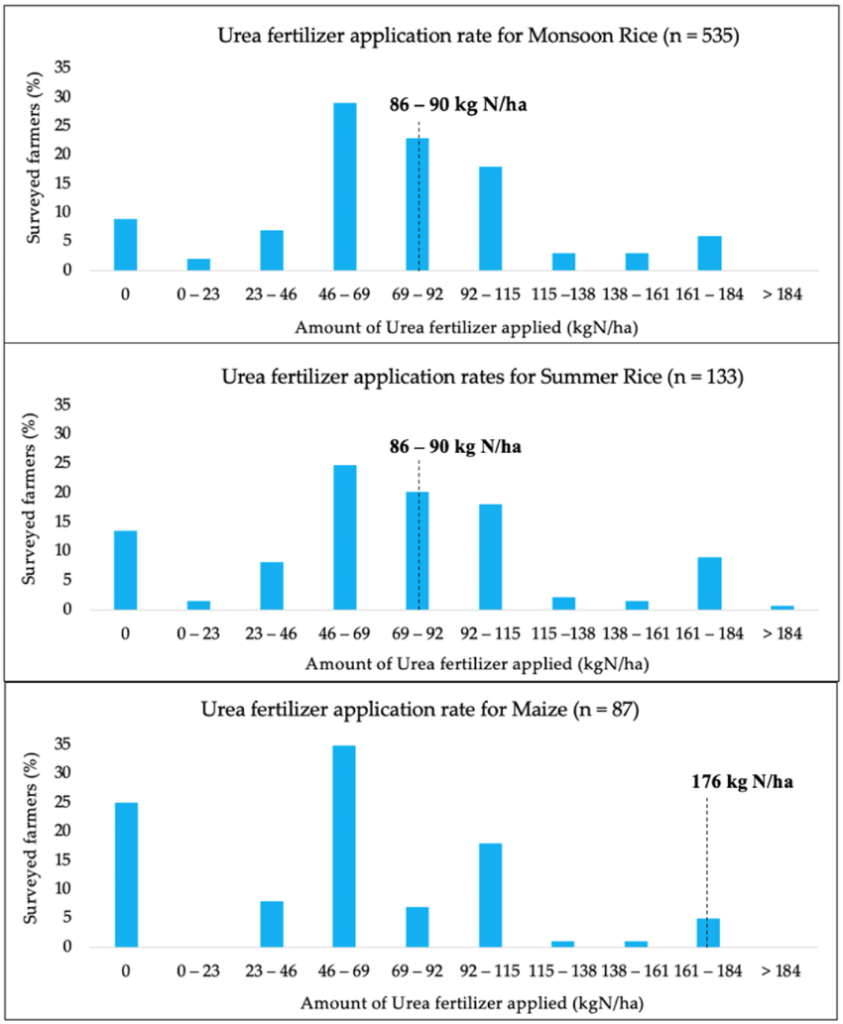
researchgate.net
Distribution of urea fertilizer application rates by surveyed farmers compared with national recommendation (—–represents the national recommended urea fertilizer application rates from Department of Agriculture (DoA) and Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation (MOAI)).
How Often to Use Urea Fertilizer : urea fertilizer how to use
It is important to note that the amount of urea fertilizer applied to trees depends on several factors, including:
- Tree age
- Tree type
- Soil condition, composition, and type
- Tree size
- Growth stage of the tree
Therefore, before beginning urea fertilization at the right time for your trees, it is advisable to consult experts, such as those at Iran Sunlight, to determine the appropriate amount of fertilizer to meet the tree’s needs and promote better growth and performance.

Methods of Applying Urea Fertilizer
Using Urea Alone
In this method, we explain how urea alone affects crops.
- Minimizing Ammonia Losses
When urea is applied on cool, cold days, ammonia loss is minimized. The best time to use urea is on a cool day with temperatures between 0 and 15°C, with little to no wind. When applied in colder temperatures, the ground is frozen, and mixing urea into the soil becomes difficult. If applied in warmer temperatures or during windy conditions, urea breaks down before it has a chance to mix with the soil, leading to nutrient loss. - Before Planting
Before planting, use urea in combination with urease (an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide). Urease starts the chemical reaction that converts urea into the nitrates needed by plants. Using urea alone before planting can result in nutrient loss before the plant can absorb it. Combining urea with urease slows down the chemical reactions and helps preserve urea in the soil. - Evenly Distribute Urea on the Soil Surface
Urea is sold in small, solid, or granular forms. You can use a fertilizer spreader to apply it evenly across the soil surface or spread the granules manually. Apply urea near the plant roots or where seeds will be planted. - Water the Soil
Before urea is converted into the nitrates plants need, it first turns into ammonia gas. Since gases easily escape from the soil surface, mixing the fertilizer while irrigating helps keep urea in the soil before chemical reactions start. This way, ammonia is trapped in the soil and doesn’t volatilize.Tip: The upper layer of soil should be moist to a depth of 1.3 cm so ammonia can stay in the soil and not escape. Don’t wait for rain; water the soil yourself or mix urea into the soil 48 hours after snow melts. - Plow the Soil to Mix Urea Thoroughly
Plowing the soil is an excellent method to mix urea thoroughly with the soil before ammonia escapes. Use a rake or tiller to incorporate urea into the top soil layer. - Monitor Nitrogen Levels in Potato Plants
Some types of potatoes can tolerate higher levels of nitrogen, while others cannot. Be cautious and avoid over-fertilizing potatoes with urea. Urea can be applied directly or as a solution with other fertilizers, provided that the nitrogen content in the solution does not exceed 30%. Solutions with over 30% nitrogen should only be used before planting potatoes. - Fertilize Legumes and Grains on Mild Days
Urea can be applied directly to most grains, but never at temperatures above 15°C, as it may result in an ammonia smell from the plant. - Apply Urea Indirectly to Corn Seeds
When applying urea to corn, maintain at least a 5 cm distance between urea and the corn seeds. Direct contact with urea can be toxic to seeds and significantly reduce corn yield.

Mixing Urea with Other Fertilizers and Enhancers
In this method, we explain how to mix urea fertilizer with other enhancers.
- Find the Ideal Fertilizer Ratio
The fertilizer ratio, indicated by the numbers N-P-K, is a three-digit number that tells you the appropriate amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) in a fertilizer. If you have tested your soil, it will show what nutrients or vitamins are deficient, and based on this, you can determine the ideal fertilizer ratio to compensate for the soil’s nutrient deficiencies. You can consult gardening centers or purchase the appropriate fertilizer for your needs. - Mix Urea with Other Fertilizers to Create a Stable Fertilizer
Urea provides nitrogen for plants, but other elements such as phosphorus and potassium are also vital for plant health. You can safely mix urea with the following fertilizers:- Calcium cyanamide
- Potassium sulfate
- Potassium magnesium sulfate
- Mix Urea with Special Fertilizers for Immediate Fertilization
Certain special fertilizers can be mixed with urea, but due to chemical reactions, their effect may diminish after two or three days. These fertilizers include:- Chilean nitrate
- Ammonium sulfate
- Magnesium nitrate
- Diammonium phosphate
- Phosphate cake
- Rock phosphate
- Mineral potassium
- Avoid Unwanted Chemical Reactions to Prevent Damage to Crops
Some fertilizers react with urea, causing either a volatile reaction or rendering the mixture ineffective. Never mix urea with the following fertilizers:- Calcium nitrate
- Calcium ammonium nitrate
- Limestone ammonium nitrate
- Ammonium nitrate sulfate
- Nitro-potassium
- Ammonium nitrate potassium
- Superphosphate
- Triple superphosphate
- Mix Urea with Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizers to Create a Balanced Fertilizer
Based on the list of effective and ineffective fertilizers for mixing with urea, choose phosphorus and potassium sources to add to your fertilizer. Many of these are available at gardening stores. Mix your chosen enhancers based on the provided weight ratios, either in a large bucket, wheelbarrow, or mechanical mixers. - Distribute Fertilizer Evenly Among Crops
Just as you applied pure urea evenly on the soil and crops, distribute the mixed fertilizer evenly. Then, water the soil and plow it to mix the fertilizer thoroughly. Since urea is less dense than other fertilizers, if using rotary equipment to spread urea on large fields, choose rows no wider than 15.2 meters for even distribution.

Using Urea in Irrigation Systems
One common question is whether urea can be used in irrigation systems, specifically sprinklers. The answer is no. Introducing large amounts of urea into the irrigation system can cause leaf burn and crop damage. It’s best to apply urea as a side-dressing before irrigation.
Urea for Saline Soils
It is generally not recommended to supply all of the plant’s nitrogen needs with urea in saline soils, as these soils have a high pH, which increases urea loss as gas.
Urea for Saline Lands
Because of its high salinity index, urea can increase salinity in the soil solution. Therefore, ammonium sulfate fertilizers are recommended for saline soils.
Biuret in Urea Fertilizer
A common impurity in urea fertilizer is biuret (C2H5N3O2), which forms during urea production. Biuret can degrade in the soil over time and cause toxicity.
Excessive concentrations of biuret in the soil can harm seedlings, so it should not be near seeds. Additionally, urea fertilizers with high biuret content should not be applied as foliar sprays as they can cause plant toxicity.
The maximum permissible biuret content for urea used in the soil is generally 2%, but this may vary depending on the plant type.
Summary Of Urea Fertilizer When to Apply
Ultimately, PetroBNX, as a company active in the export and sale of various chemical and mineral fertilizers, with a special focus on urea, understands the importance of proper and optimal use of this fertilizer for better agricultural productivity. Urea, as one of the main sources of nitrogen for plants, has widespread applications in agriculture, but its proper use depends on several factors, including soil type, plant type, and environmental conditions.
PetroBNX recommends selecting the appropriate N-P-K ratio for the soil to achieve the best results and using a balanced mix of urea with other fertilizers. Additionally, paying attention to the specific conditions of saline soils and being cautious about the amount of urea used in irrigation systems is crucial.
The company also ensures product quality by monitoring the level of biuret in urea fertilizers, striving to offer products of high quality that are not harmful to soil and plants. Ultimately, the correct use of urea and its combination with other fertilizers can lead to better plant growth and optimal agricultural performance.




No comment