Viscosity Grade Bitumen, commonly referred to as VG Bitumen, is a specific classification of bitumen characterized by its viscosity measurements rather than penetration tests. This grading system was introduced to predict bitumen behavior at varying temperatures, offering greater accuracy and reliability compared to the traditional penetration testing method.

Key Characteristics of VG Bitumen
Grading System: VG Bitumen is divided into four grades—VG10, VG20, VG30, and VG40—based on its viscosity levels. Higher grades correspond to stiffer bitumen.
Testing Method: Viscosity testing measures bitumen’s ability to flow at both 60°C (representing peak summer conditions) and 135°C (mixing temperature). These precise measurements ensure consistent performance across applications.
Comparison to Penetration Testing: Viscosity testing has replaced several outdated tests, such as specific gravity and ductility, as these were found unrelated to the product’s real-world performance. The transition from penetration grading to viscosity grading enhances the predictability and reliability of bitumen under diverse conditions.
Applications of VG Bitumen
Viscosity Grade Bitumen is widely used in paving, road construction, and manufacturing asphalt pavements. Its durability and adaptability make it suitable for various climates and traffic conditions:
- VG-10: Ideal for cold climates, surface dressing, and producing bitumen emulsions and modified products.
- VG-20: Designed for high-altitude regions with cold climates.
- VG-30: Preferred for heavy-duty pavements requiring resistance to significant traffic loads.
- VG-40: Used in high-stress areas like toll booths, intersections, and truck parking lots due to its superior resistance to shoving and deformation.
Advantages of VG Bitumen Over Penetration Bitumen
Performance Consistency: Viscosity Bitumen ensures uniform rutting resistance across similar viscosity grades, unlike penetration grades.
- Temperature Susceptibility: The grading system specifies minimum kinematic viscosity at 135°C and penetration at 25°C, offering better control over temperature susceptibility.
- Enhanced Durability: VG Bitumen’s properties minimize tender mixes and improve fatigue resistance, making it suitable for a wider range of temperatures and conditions.
- Accurate Mixing and Application: By measuring viscosity at two temperatures, suppliers can provide precise mixing and application guidelines.
- Global Preference: The VG grading system is internationally recognized for its accuracy and reliability, making it a preferred choice in countries like India and Australia.
Technical Insights into Viscosity Testing
Two Types of Viscosity Measurements:
Absolute Viscosity: Measures resistance to flow at 60°C, representing bitumen’s behavior during summer conditions.
Kinematic Viscosity: Represents the viscosity-to-density ratio at 135°C, critical for understanding bitumen’s performance during asphalt mixing.
Grading Standards:
AASHTO (American Association of State Highway Officials) defines two systems:
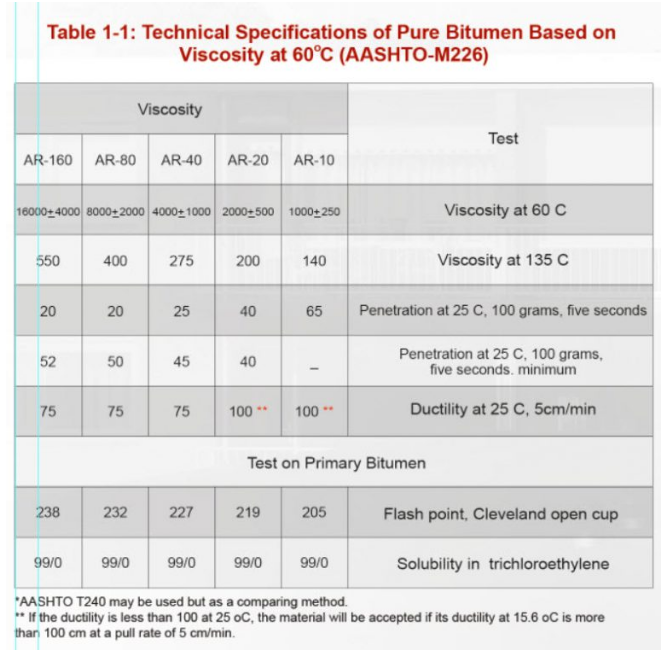
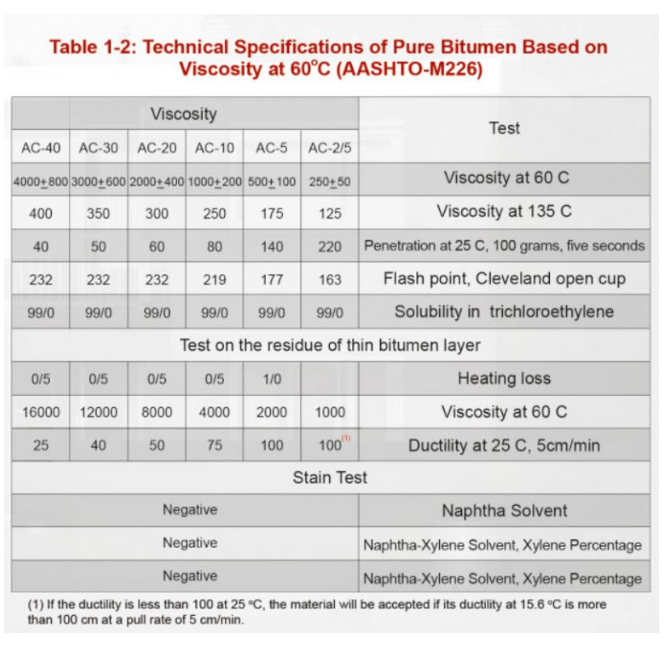
- Standard Viscosity Grade (AC Grades): Evaluates bitumen at 60°C. Grades range from AC-2.5 (softest) to AC-40 (hardest), used in climates varying from cold to hot.
- Aged Residue Grades (AR Grades): Tests viscosity on aged residue samples at 60°C.
Conclusion
Viscosity Grade Bitumen, developed in the 1970s, revolutionized the classification of bitumen by focusing on its functional properties and behavior under varying conditions. The VG grading system allows for precise applications, making it a preferred choice for traders and engineers worldwide. By ensuring durability, flexibility, and reliability, VG Bitumen has become a cornerstone of modern road construction and asphalt paving projects.
For more information or to source premium Viscosity Grade Bitumen, contact PetroBNX, a trusted supplier in the industry.
Technical Specification of Pure Bitumen Based on Viscosity on 60 C (AASHTO M-226)
Performance Grade Bitumen
Performance Grade (PG) Bitumen is bitumen which is graded based on its performance at different temperatures. In Superpave grading system, binders are classified according to their performance in extreme hot and cold temperatures and called as performance grade (PG) bitumen.
Penetration Grade Bitumen
Penetration Grade Bitumen is a standard bitumen usually used as a Paving Grade Bitumen essential for road construction and for the production of asphalt pavements with superior properties, and it’s very important once it bounds the aggregates and creates a unique cohesion and stability to the bituminous mix.





No comment